Post Time: 2025-09-01
Understanding Prediabetes: What Blood Sugar Levels Indicate This Condition
Prediabetes is a precursor to type 2 diabetes, characterized by blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), prediabetes is defined as a fasting plasma glucose level of 100-125 mg/dL or an HbA1c level of 5.7-6.4%.
The Dangers of High Blood Sugar Levels
Elevated blood sugar levels can have serious consequences on overall health, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and even nerve damage. Moreover, high blood sugar can also lead to fatigue, blurred vision, and an increased thirst.
Blood sugar fluctuations are often caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. For instance, individuals with a family history of diabetes or those who engage in sedentary lifestyles may be more prone to developing prediabetes.
Managing Blood Sugar: A Balanced Approach
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels requires a balanced approach that incorporates diet, exercise, and stress management techniques. Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body effectively regulate glucose levels.
A healthy diet plays an essential role in managing blood sugar levels. Foods high in fiber such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes help slow down sugar absorption into the bloodstream. On the other hand, refined carbohydrates and sugary drinks should be consumed sparingly or avoided altogether.
Stress Management: A Key Factor
Chronic stress can have a negative impact on blood sugar levels by releasing cortisol hormones that promote glucose release from storage sites in the body. Practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate this effect and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise also plays an essential role in regulating blood sugar levels. As excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, shedding pounds can improve glucose regulation.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: A Crucial Tool
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing prediabetes effectively. This involves checking your fasting plasma glucose level upon waking and at regular intervals throughout the day using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Early Intervention: A Key to Prevention
Identifying prediabetes early on allows for timely intervention and prevention strategies. If you are at risk of developing prediabetes or have been diagnosed with it, consult your healthcare provider about ways to manage blood sugar levels effectively. Regular check-ups and monitoring can help identify any significant changes in glucose regulation.
Early detection also provides an opportunity to implement lifestyle modifications that improve insulin sensitivity and overall health outcomes.
Glycemic Index: A Measure of Carbohydrate Impact
The glycemic index is a measure used to evaluate the effect of different carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI value are gradually absorbed into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in glucose levels. Understanding how different foods affect your body can help you make informed choices about meal planning and managing prediabetes.
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels requires ongoing commitment and patience but offers numerous benefits for overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Prediabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels (100-125 mg/dL or HbA1c 5.7-6.4%).
- High blood sugar can lead to serious health complications.
- Balanced lifestyle habits, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, are essential for managing prediabetes.
- Stress management techniques like yoga and meditation can help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Actionable Tips
1. Consult your healthcare provider about monitoring your fasting plasma glucose level.
2. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises to manage stress.
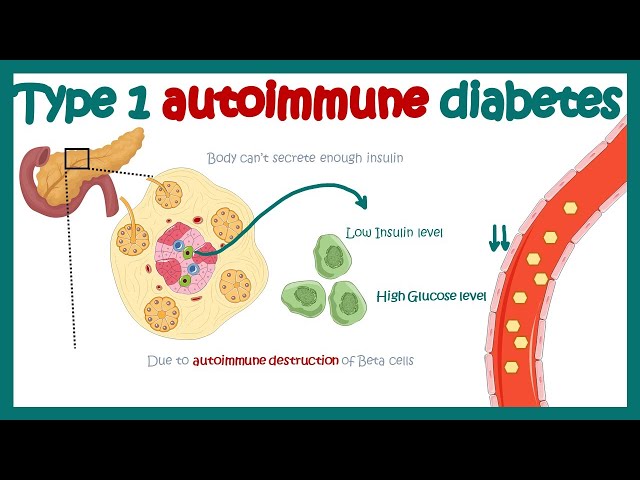
A chronic condition in which the pancreas 110 blood sugar fasting produces little 3 month average blood sugar test range or no insulin. It typically appears in adolescence. Symptoms include increased zenfit blood sugar support reviews thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue and blurred vision. Treatment aims at maintaining normal blood sugar levels through regular monitoring, insulin therapy, diet and exercise.