Post Time: 2025-09-01
Unlocking Stable Blood Glucose: The Power of Fiber-Rich Diets
Fiber-rich diets have been touted for their numerous health benefits, from promoting digestive regularity to supporting healthy weight management. However, a lesser-known benefit of consuming fiber-rich foods is its impact on blood glucose levels. Research has shown that incorporating more fiber into one's diet can lead to improved insulin sensitivity and better-regulated blood sugar.
When it comes to maintaining optimal blood glucose control, the type and quantity of carbohydrates consumed play a significant role. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars during digestion, which then enter the bloodstream, causing blood glucose levels to rise. Insufficient fiber intake allows these carbohydrates to be quickly absorbed by the body, leading to rapid spikes in blood sugar.
Balancing Blood Glucose with Fiber-Rich Foods
One of the primary ways that fiber-rich foods contribute to stable blood glucose is through their ability to slow carbohydrate absorption rates. High-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain complex carbohydrates that are not readily absorbed by the body. This means that as they enter the digestive system, they interact with beneficial gut bacteria, promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
Studies have demonstrated that individuals consuming high amounts of dietary fiber tend to experience reduced fluctuations in blood glucose levels compared to those consuming lower-fiber diets. By incorporating more whole foods into one's diet and limiting refined or processed carbohydrates, it is possible to significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
The Fiber-Blood Glucose Connection: How It Works
Dietary fiber plays a critical role in blood glucose control through several mechanisms. Firstly, high-fiber foods help regulate digestive motility by encouraging regular bowel movements. This reduces the amount of undigested carbohydrates available for absorption and subsequent utilization by the body.
In addition to its impact on digestion, dietary fiber also promotes satiety, reducing overall food intake and minimizing overconsumption of simple sugars that can lead to rapid blood glucose spikes. Furthermore, beneficial gut bacteria fermentation products such as short-chain fatty acids have been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity.
Optimizing Fiber Intake for Better Blood Glucose Control
While incorporating more fiber-rich foods into one's diet is a great step towards optimizing blood glucose control, it's equally important to consider the type and quantity of dietary fiber being consumed. The recommended daily intake varies from 25 grams per day in general populations to as high as 50-80 grams for individuals with pre-existing gastrointestinal disorders.
For optimal results, choose whole foods such as fruits (berries, apples), leafy greens (spinach, kale), legumes (lentils, chickpeas) and fiber-rich grains like quinoa or brown rice. Limit intake of highly processed cereals that may be high in added sugars but low on essential nutrients.
From Fiber to Better Health: How Blood Glucose Control Affects Overall Well-being
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is not only crucial for minimizing the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, it also plays a significant role in maintaining optimal mental health. Improved insulin sensitivity has been linked with better cognitive function, improved mood regulation and reduced symptoms associated with depression.
Furthermore, evidence suggests that controlled blood sugar may enhance overall quality of life by promoting sustained energy levels throughout the day. Incorporating fiber-rich foods into one's diet is just one aspect of managing stable glucose control but a fundamental step in protecting against long-term health complications.
Navigating the Complexities of Blood Glucose Control with Fiber-Rich Diets
Blood glucose management involves intricate factors including meal timing, exercise patterns and lifestyle habits that can impact overall dietary efficacy. Establishing a consistent routine for fiber consumption allows individuals to appreciate its profound benefits on regulating blood sugar levels over time.
However, as tempting it may be to completely overhaul one's diet by drastically increasing daily fiber intake overnight or replacing every other nutrient-dense food with supplements - patience is key here! Gradual changes such that gradual adjustments in lifestyle contribute significantly towards more lasting impact.
Practical Strategies for Boosting Fiber Intake and Optimal Blood Glucose
Implement small yet intentional dietary alterations each day, gradually introducing whole foods high in fiber into meals. Incorporate different colors on your plate to prioritize the intake of a variety of fruits and vegetables that support blood glucose control.
As consumers delve deeper into creating effective meal plans tailored towards their nutritional goals it is also beneficial they take note how portion sizes can make an impact when trying maintain optimal amounts daily consumption limits for essential nutrients should never be pushed too far, yet moderate lifestyle adjustments over long term truly pay off in a lasting sense.
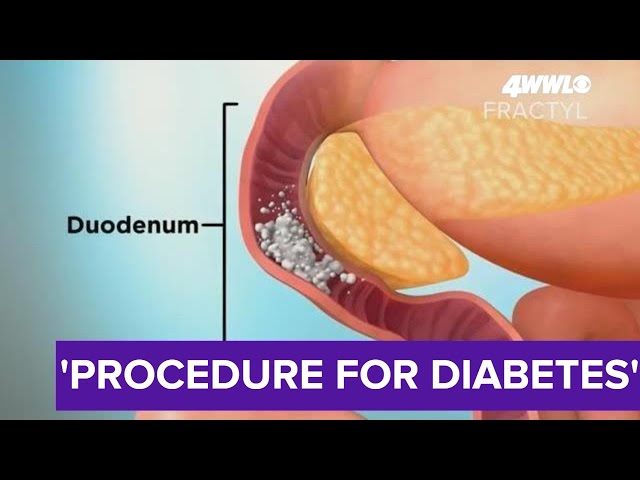
Doctors in New Orleans are testing a procedure they call “surgery for diabetes.” It's something they balancing blood sugar levels naturally believed until recently, was unheard how much sugar in a blood orange of. Now local people with diabetes will have the chance to be among the first in the U.S. to join the clinical trial. Thirty years ago, gastric bypass surgery was popular for weight loss. The stomach was made smaller, then connected to a lower part of the 6.6 blood sugar conversion small intestines. So food would no longer go through the duodenum. That's the first foot of the small intestines. Then something unexpected emerged. MORE: