Post Time: 2025-09-01
Blood Sugar Level: What It Means for Your Overall Health
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for your overall well-being. When we talk about ideal blood sugar levels, most of us are unaware that it varies depending on various factors such as age, health conditions, and even the time of day.
Understanding Normal Blood Sugar Range: Factors to Consider
When determining if your blood sugar range is within normal limits or not, consider what's considered a normal blood sugar range for adults. For most healthy individuals without diabetes, fasting blood glucose levels typically fall between 70-99 mg/dL. However, it's essential to note that this can fluctuate based on factors such as age and physical activity level.
The Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Blood Sugar Range
Exercise plays a significant role in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Physical activities help lower your blood glucose by increasing insulin sensitivity – the body becomes more efficient at using its own insulin, thereby lowering overall glucose concentrations.
However, some people might experience increased stress and anxiety which negatively impacts their ability to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Stress can cause an increase in cortisol production, a hormone known for raising your appetite while impairing insulin's effectiveness by making it harder for the body to absorb glucose into cells efficiently – thus elevating that all-important HbA1c measurement significantly impacting long-term control.
Stabilizing Blood Sugar Through Nutrition
Certain foods have shown promise in helping stabilize blood sugar ranges and promote a healthier overall digestive system such as fiber-rich foods. Foods with low glycemic indices like whole grains, fruits, and leafy greens also help slow down the digestion process allowing your body to take its time absorbing glucose from these nutritious sources into bloodstream.
Incorporating stress-reducing activities along healthy dietary habits can improve insulin sensitivity significantly over a short span thereby achieving long-term blood sugar control results.
Understanding How Diet Impacts Blood Sugar Levels
To better understand how high or low you're running, incorporating specific food items like protein and fiber-rich foods will slow down digestion. Protein helps build muscle mass while also aiding in nutrient absorption slowing overall gut movement thus giving your system time to digest glucose efficiently.
By adjusting what we put into our bodies through meal planning tailored specifically around controlling blood sugar levels can improve insulin sensitivity significantly – keeping it within an ideal range for sustained period.
Stabilizing Blood Sugar Through Healthy Exercise Habits
Exercising also boosts your body's ability to manage its own natural fluctuations by promoting better insulin usage at a cellular level, lowering overall glucose concentrations in bloodstream due improved metabolic performance as cells start using blood sugar more efficiently resulting lower spikes during postprandial state.
Importance of Sleep for Regulating Blood Sugar Levels
Sleeping less or not well enough may significantly impair your body's ability to keep these levels from getting too high thereby leading higher risk for chronic conditions such heart disease kidney failure obesity stroke nerve damage even eye and foot problems.
When our bodies aren't getting enough restful sleep it causes blood glucose level fluctuations – a sign that needs prompt medical attention especially if symptoms persist or worsen.
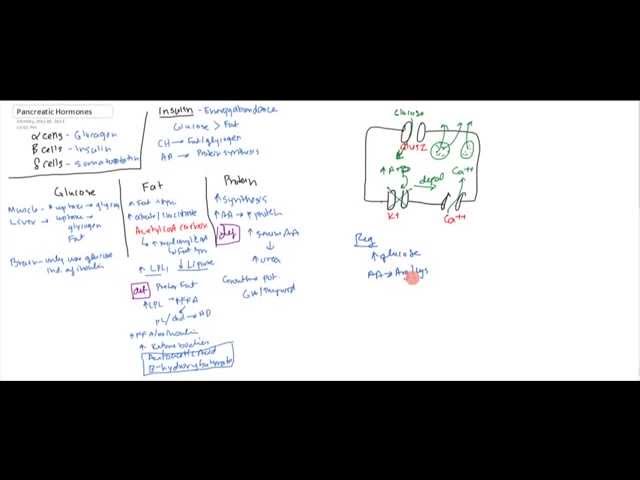
The endocrine pancreas hormones such as Insulin, Glucagon, and somatostain physiology and pathophysiology explained for USMLE Step 1. is made up of 3 types of cells. Alpha cells secrete glucagon, Beta cells secrete insulin and Delta cells secrete somatostatin. INSULIN Generally speaking insulin is designed for energy abundance. So your body prefers to use glucose rather than fats for energy. The body will use CH instead of fat and glycogen. And use Amino Acids for protein synthesis. GLUCOSE Muscle will have increase uptake to make glycogen in the muscle. In the liver it will be used for uptake to use for glycogen and can beets lower blood sugar fat. Brain will only does coconut water raise blood sugar use glucose and this is independent of insulin. FAT Increase fat storage. Increase citrate and isocitrate. Increase AcetylCoA Carboxylase. This increase malonyl CoA which will increase Fat synthesis. This will increase Lipoprotein lilpase and decrease lipase. In Deficiency you prefer fats so you increase lipoprotein lipase which increase Free Fatty Acids. This will become phospholipids and cholesterol leading to heart disease. When there is Free Fatty Acids without insulin this will increase Ketone bodies (Acetoacetic Acid and B-hydroxyacetate). PROTEIN Increase synthesis and storage of protein. Increase AA and Increase Protein synthesis. In deficiency there is increase serum AA and increase urea in urine. It also increase effect on Growth Hormone. MECHANISM OF ACTION of BETA Cell When Glucose comes in this increases ATP and blocks Potassium channel. This depolarizes and causes opening of signs of high blood sugar and low blood sugar Calcium channel. Regulated by glucose, Amino Acids, and GIT hormones. GLUCAGON This hormone is expressed when glucose is low. Therefore it will increase gluconeogenesis by converting Amino acids into glucose and converted fats into glucose. Increase cAMP which will increase Phorphokinase which will increase phorphorylase and increase glucose phosphate. Only small amount of glucose is necessary to have greater effects because of amplification. At really high concentrations it can increase heart contraction, increase blood flow to organs, increase bile secretion an block gastric acid. SOMATOSTATIN REgulated by high glucose, Amino Acids, Fatty Acids and GIT hormones. Effects of somatostatin - decrease insulin and glucagon. Decreases motility of duodenum, stomach and gallbladder. Decreases secretion and absorption in GIT.